Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease that affects a person’s skin, nail plates and joints. The disease is characterized by a wavy course with periods of worsening and remission. The risk of this disease lies not only in the unpleasant sensations it causes, but also in the fact that the disease greatly complicates life, interfering with social adjustment and a normal quality of life. In severe cases, severe depression can result from the acute form of the disease.
How to get rid of psoriasis, what is this disease, what are the symptoms and treatment of psoriasis? You will learn about this from our article.
Psoriasis: causes
Under normal conditions, the skin of a healthy person is renewed within a month. During this time, the dead cells stratify, and new sites take their place. If there is a malfunction in the skin rejuvenation mechanism, the process of maturation of new cells takes only about a week, which disrupts the cellular balance. As a result, cells die much faster.
In the areas affected by the pathological process, there is an excessive proliferation of immune system cells, macrophages and epithelial tissue cells. Due to this, the skin exfoliates and creates favorable conditions for the inflammatory process. In addition, the processes of formation of new capillaries are accelerated, therefore the skin at the site of inflammation becomes red.
Chronic psoriasis is non-infectious in nature, so the disease is considered non-infectious. This was created as early as the 19th century, but so far scientists can not name the exact reason for its occurrence.
Among the reasons that are prerequisites for the development of the disease, there are:
- Inheritance. If a person’s parents or close relatives have a predisposition to skin pathologies, it is very likely to be inherited. This is due to a mutation in some pieces of DNA that was found among patients suffering from psoriasis and a similar mutation that was found in their loved ones.
- Gene mutations. Violations in the structure of DNA, which affect the violation of skin renewal processes, can not only be inherited, but also manifest at a later age in people whose relatives do not suffer from psoriasis. It is not known what causes such gene changes.
- Weakening of the immune system. Any violation of the body's defenses can trigger psoriasis.
- Disruptions in metabolic processes. Metabolic disorders manifest in the form of changes in the metabolism of fats, nitrogen, carbohydrates and vitamins in psoriasis. As a result, there is an accumulation of toxins in the body, a decrease in adaptive abilities and an increased susceptibility to infections. Also, patients have an increase in bile acid fractions in the blood serum, caused by metabolic disorders.
- External stimuli. Friction, constant contact with chemicals, wearing tight clothing, cuts and insect bites - all of these cause microtraumas to appear on the skin, which over time can develop into psoriasis.
- Frequent allergic reactions. If a person has a tendency for atypical immune system reactions, manifested in the form of skin rashes, itching and rashes, this is an additional opportunity to get psoriasis.
- Strong experiences or prolonged stressful situations. Any stress causes a weakening of the body's defenses and undermines the immune system. If a person has a tendency to skin diseases, it can appear at exactly such moments. In addition, any stress affects endocrine processes, due to which significant doses of adrenaline and norepinephrine are released into the bloodstream. This process affects metabolic processes and biochemical reactions, becoming a prerequisite for the development of psoriasis.
- General weakness of the body caused by serious pathology - atherosclerosis, cirrhosis of the liver, diabetes, hypertension, etc.
- Unbalanced diet and alcohol abuse. If a person eats a lot of fatty, smoked, salty, sweet and spicy foods, the chances that they may develop psoriasis increase. Also, in some cases, a prerequisite for the development of the disease is the excessive consumption of chocolate and citrus fruits.
- Hormonal increases caused by serious changes in hormonal levels during menopause, puberty, pregnancy, lactation, after abortion. It is worth noting that the hormonal cause of psoriasis may not be related to the periods shown above. In this case, we are talking about changing the functioning of the organs of the endocrine system.
- Climate change, living in adverse environmental conditions. If a person is prone to psoriasis and moves to a colder area, the disease can worsen significantly. The same goes for staying in areas with highly polluted air and water. However, the climatic factor can hardly be called the main cause of the disease: on the contrary, it acts as a catalyst that activates the "dormant" form of the body prone to psoriasis.
How to determine if it is psoriasis: symptoms of the disease
First, psoriasis is a skin condition. However, in some, especially severe cases, it can affect not only the skin but also the tendons, internal organs, spine, nail plates and joints. Below we will look at the signs of psoriasis that appear in the first place and allow you to distinguish psoriasis from other skin pathologies.
How does psoriasis start?
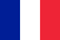
On the surface of the skin (most often on the knees, hands, elbows, back, armpits, under the breast, in the sacrum region, on the genitals) and sometimes on the mucous membranes, dry rounded red areas appear. Initially, their size is relatively small: each papule is only a few millimeters in diameter. However, over time, the affected areas grow, the papules join together and form so-called psoriatic plaques: their diameter reaches 10 cm and even more.
Initially, papules do not cause obvious discomfort to a person. They practically do not itch or itch. However, over time, as they grow and plaque builds up, the affected areas thicken and rise slightly above the healthy areas of the skin. This phenomenon is accompanied by itching.
A characteristic feature of psoriasis in the initial stage is the formation of small dry scales with a loose structure in the affected areas of the body. Their color varies from white to yellow-gray, and a thin pink-red edge can be seen around each tile. Outside, these areas are a bit like molten paraffin, for which they are called "paraffin lakes".
At first, the signs of psoriasis on the skin of the body and face can be confused with manifestations of eczema or other skin pathologies. The stage of psoriasis - the so-called psoriatic triad - helps determine the type of disease.
- Stear stain phase. It is characterized by the formation of characteristic flakes similar to stearin, which appear when the plate is broken.
- Terminal film phase. It looks like a smooth, moist, glossy red surface found under the scales.
- The "blood dew" phase. If a person begins to remove the terminal film, small drops of blood form on its surface, caused by the exact bleeding. On the other hand, it is caused by thinning of the vascular network and fragility of the capillaries.
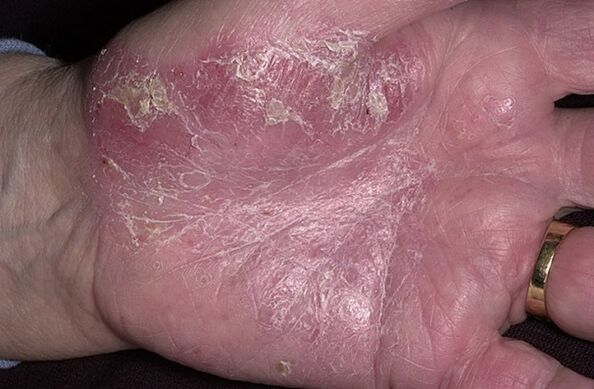
The onset of psoriasis is also associated with non-skin related symptoms. Usually, patients complain of increased fatigue, apathy, irritability, drowsiness, mood swings, dizziness, nausea and sleep problems.
How does psoriasis appear, other than skin lesions?
This disease affects not only the skin but also other organs and systems. The following manifestations and forms of psoriasis are distinguished:
- Psoriatic arthritis. In some cases, the lesion is localized not in the upper areas of the skin, but much deeper. As a result, the disease spreads to the joints. The course of the disease is in many ways similar to the development of rheumatoid arthritis, but there are a number of differences between them. For example, in psoriatic arthritis, asymmetric joint damage is usually observed, the greatest peak of concern occurring in the morning, but the main difference is that rheumatoid factor is absent in the blood of patients with psoriatic arthritis.
- Muscle damage. If the disease is at an extremely advanced stage, muscle tissue atrophy can occur after cartilage and joint damage.
- Liver dysfunction. The task of the liver is to cleanse the blood and remove harmful substances. If there is an increase in the content of toxins in the body, characteristic of psoriasis, the liver suffers from this in the first place.
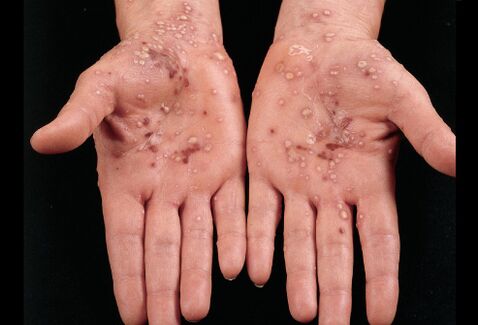
- Transmission of the disease from the skin to the mucosa. If the disease is not treated, it progresses and passes to the mucosa of the cheeks and genitals, to the lips and tongue. The mucous membranes swell, causing foci of inflammation, accompanied by desquamation.
- Damage to the nail plates (psoriatic onychodystrophy). Psoriasis often affects the nails. The disease manifests itself in the form of thickening of the nail plates on the hands and feet, a change in their color, the appearance of grooves and spots on them. Inflammatory processes affecting the skin around the nails, hemorrhage under the nail plate, dryness, delamination and increased brittleness of the nails can also be observed. In particularly severe cases, we can talk about the complete detachment of the nail and its loss.
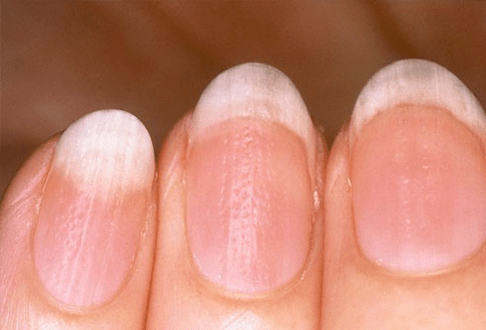
As you can see, this disease is quite dangerous, therefore, its treatment should begin as soon as possible in order to prevent its transfer to other organs and systems.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Since the disease is non-infectious and non-viral in nature, it is not contagious at all. The only way of transmitting the disease is a genetic predisposition caused by heredity.
Types of psoriasis
There are several types of this disease, each of which has its own course characteristics and characteristic symptoms.
- Simple / vulgar / slab / slab / ordinary. According to the International Classification of Diseases - prosiasis vulgaris. This form is more common than others: in about 80-90% of cases of the disease, it is psoriasis vulgaris. It is characterized by the appearance of "paraffin lakes" or psoriatic plaques.
- Inverse (inverse psoriasis). This type of disease mainly affects the skin folds, the outer surface of the thighs, the hip area with the external genitalia. The main difference between reverse psoriasis and vulgar psoriasis is that with the opposite form of the disease, plaque does not form on the skin: the skin becomes covered with red spots, accompanied by an inflammatory process. The danger of reverse psoriasis is that it progresses with sweating and rubbing. Because of this, microcracks form on the skin, into which the infection enters. As a result, it can lead to skin lesions with cocci and fungi.
- In declining form (according to ICD - gut psoriasis). Its difference from other varieties is that the rash with tear-shaped psoriasis does not coalesce into large plaques. The patient's body is covered with small spots that resemble dots (hence the name of the disease), the color of which varies from pink to purple.
- Pustular / exudative. If other types of the disease are characterized by dry areas of the skin, then pustular or exudative psoriasis may be recognized by weeping blisters filled with a clear fluid. In this case, the skin around the blisters usually becomes red, the local temperature rises. If the blisters burst or the patient combs them, there is a risk of infection and subsequent suppuration - this is the main risk of the pustular form of the disease.
- Psoriatic erythroderma. This is one of the most severe forms of the disease, which, if the course is unfavorable, can lead to the death of the patient. Its distinguishing feature is the exfoliation of the skin, as a result of which infection with pathogenic microflora can occur. The first signs and symptoms of this type of disease - psoriasis manifests itself in the form of severe itching of the skin, small red scaly red rashes, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling of tissues and an increase in overall body temperature in38-39 degrees. It is divided into generalized and hyperergic types.
- Seborrheic psoriasis. Most often, this type of disease affects the scalp, but in some cases may include nasolabial folds, the skin near the ears, and the shoulder blade area. It is characterized by the appearance of dandruff (when localized on the head), severe itching and a gray bloom.
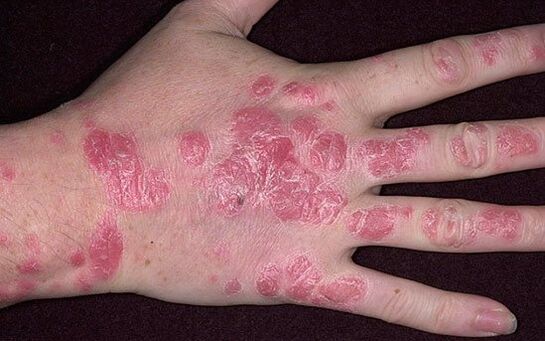
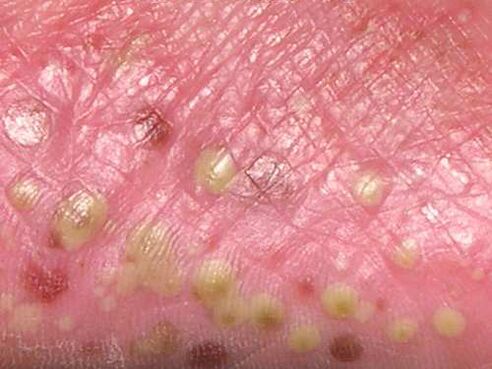
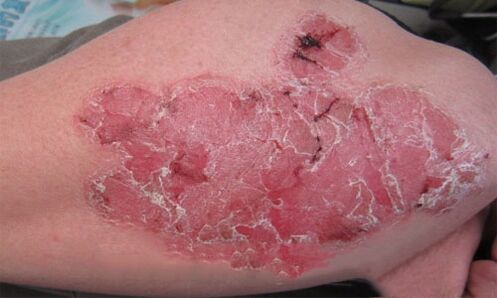
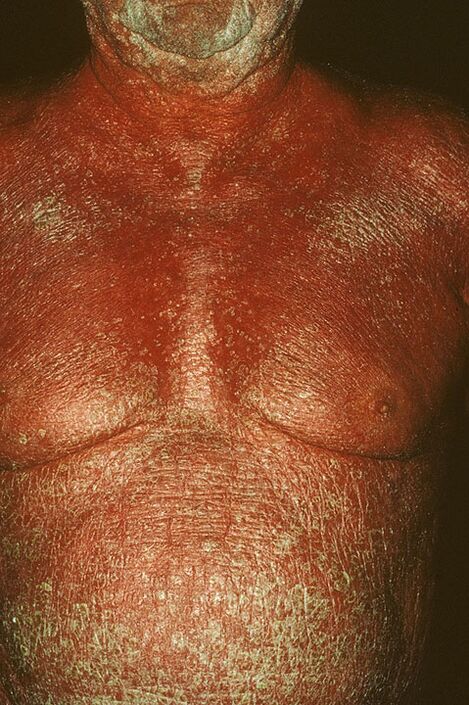
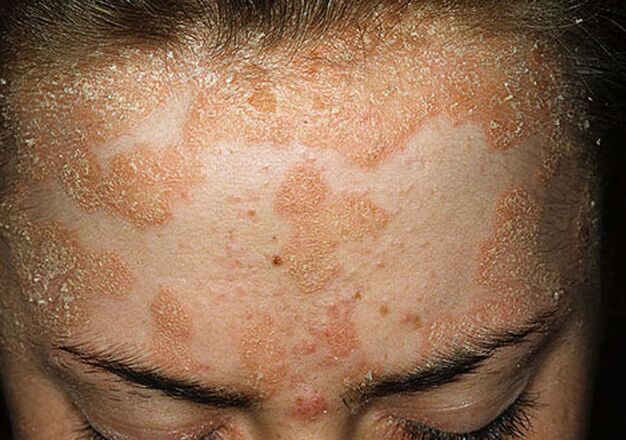
Worsening of psoriasis
The disease is characterized by a chronic course of swell with periods of worsening and remission. A decrease in the intensity of symptoms is usually observed in the warm season, while the disease worsens in winter and autumn.
Factors that provoke a worsening of the disease may be:
- Stress, anxiety.
- Unbalanced working and rest hours.
- Weakening of the body after suffering an infectious or viral disease.
- A sharp jump in hormones.
- Taking some medication.
- Use of inappropriate cosmetics.
- Skin contact with household chemicals.
- Malfunction of organ systems.
- Exposure to extremely dry, hot or cold air.
- Personal hygiene is not guaranteed.
- Insect bites.
- Worsening of allergic reactions.
- Wearing tight synthetic clothes.
- Transition to an unusual climate.
Exacerbation of any skin disease (including psoriasis) brings the patient major concerns - not only physical but also to a greater psychological extent. The quality of life of a person suffering from severe psoriasis in the acute phase is significantly reduced.
Patients with psoriasis often have obvious difficulties and problems with social adaptation, which can negatively affect work / school / personal life. A person refuses contact with others, preferring to spend most of his time alone. As a result, he develops social anxiety, which can develop into severe depression over time.
An exacerbation of the disease can lead to the fact that it becomes difficult for the patient to take care of himself and his loved ones, lead a normal life and even sleep. If the rash is localized in the genital area, they can cause physical and psychological discomfort and cause partners to refuse intimacy.
Severity of the disease
Depending on the area of skin affected and the spread of the lesion to the joints, nails and internal organs, a mild, moderate and severe form of the disease is released.
- The mild form implies minor damage to the skin, when the total area of the lesion is about 3%.
- Loss of 3 to 10% of human skin is considered a moderate severity of the disease.
- A severe degree implies a significant skin lesion - by 10% or more of the total skin area.
If a patient is diagnosed with damage to the joints, muscles and internal organs, we are talking about a severe form of the disease, even if there are virtually no plaques and papules on the body.
How to eliminate psoriasis: treatment
The question of how to cure psoriasis forever is troubling to all people suffering from this disease. The fight against external manifestations of the disease gives only a temporary result, therefore, in order for the effect to be long-term, it is important to eliminate the causes of psoriasis. This usually takes a long time - up to a few years. The patient must be patient, but only in this case he can count on a long-term effect.
Below we look at how to treat psoriasis with medication, hormone therapy, phototherapy, exercise. We also turn to methods of treating psoriasis with folk remedies - in combination with traditional therapy, traditional medicine can give tangible results.
Treatment of psoriasis with medication
The first thing to do after finding suspicious round rashes, increased dryness and peeling skin on yourself or your loved ones is to seek qualified medical help. Only a dermatologist can determine exactly what kind of skin damage is happening in your particular case. Remember: under no circumstances should you treat yourself, as lack of therapy or self-selected medications can cause serious damage to your health.
There is usually no need for tests or skin tests to diagnose the disease. It is enough for the doctor to see the skin covered with papules or plaques in order to determine the cause of the lesion. If there is a serious form of the disease, the dermatologist may prescribe a recommendation for tests - general and biochemical studies of blood and urine, and in particularly severe cases, a skin biopsy may be required. X-rays may be needed to diagnose psoriatic arthritis.
There are several effective treatments for psoriasis. Choosing the right therapy option depends on the degree of damage to the skin, joints, nails, and the intensity of the disease progression. Usually, the best option is to choose a comprehensive treatment regimen that includes the use of local and home remedies, the use of ultraviolet radiation, bathing in salt and soda baths, and physical therapy.
Creams, gels, oils, sprays and lotions are used to eliminate the itching and shaking of damaged skin. They can be made on the basis of salicylic acid, pyrite, tar and other active ingredients. The main task of external hormonal and non-hormonal preparations is the softening of psoriatic plaques, disinfection, elimination of inflammation, moisturizing and nourishing the affected areas of the skin.
In the role of orally administered drugs in the treatment of psoriasis in humans, there are drugs based on efalizubam, gamma-D-glutamyl-D-tryptophan sodium, etc.
A positive result in the treatment of skin psoriasis gives a break at sea. At the same time, it is advisable to choose resorts with a relatively mild and warm climate. The ideal solution is treatment in specialized sanatorium and spa institutions, the rest of which aims at the complex therapy of psoriasis.
Psoriasis: home treatment
Treating psoriasis with home and folk remedies can only be effective if it acts as an adjunct therapy that complements the main medication treatment. Also, a bet on traditional medicine prescriptions can be made if the patient has allergic reactions to the medication. But in any case, what to do with psoriasis should be decided by the doctor, so if you want to use this or that popular method, be sure to consult a dermatologist.
One of the most common traditional remedies for psoriasis is the use of baking soda. Sodium bicarbonate has a soothing effect on psoriatic plaques, soothes rough skin, reduces itching and improves waste removal. On the basis of soda, household oils, baths are prepared, soda is taken orally, compresses and lotions are made.
Also, salt baths are an effective method of treating the disease. They become a worthy alternative if the patient does not have the opportunity to travel by sea.
Celandine juice applied to psoriatic tablets also gives positive results. However, you need to remember that this medicine is quite aggressive, so you need to make sure that the fluid does not get into healthy areas of the skin.
Walnut shells are also used to fight psoriatic plaques. The shell is poured with boiling water, after which it is insisted, the resulting infusion is filtered and added to a warm bath. This medicine is especially effective during periods of disease exacerbation.
How to cure psoriasis with diet?
Proper nutrition plays an important role in all skin conditions, and psoriasis is no exception. Of course, a balanced diet may not be a one hundred percent cure for psoriasis, but in combination with traditional medicine and medicine, it gives good results.
During treatment, as well as to extend the period of remission, doctors recommend to abstain from alcohol, smoked and salty foods, fatty and spicy foods, the use of artificial flavors, preservatives, emulsifiers and chemical dyes, fatty meats, mayonnaise, ketchup. It is also advisable to reduce the amount of salt, refined sugar, chocolate and other sweets consumed. Doctors advise you to focus on using low-fat fermented dairy products, plant foods, whole grains, lean meats and fish.
Despite the fact that during the diet it is desirable to reduce the amount of fat consumed, it is unreasonable to completely abandon them. You just have to replace animal fat with vegetable oils - olive, flaxseed, corn, sunflower.
Prevention of psoriasis
The treatment stages of psoriasis necessarily include a remission period. It is important to extend these periods as long as possible. To do this, the patient must follow a number of rules for disease prevention:
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Refuse to wear tight clothes made of wool and synthetic materials.
- Spend plenty of time outdoors.
- Provide adequate rest and adequate sleep.
- Take good care of your skin.