Psoriasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Psoriasis is a chronic non-communicable disease that can affect various organs: skin, joints, heart, kidneys.
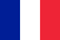
Most often, mild psoriasis appears on the skin as well-defined pink-red papules (nodules that rise above the surface of the skin), which join into plaques with white-silvery scales.
In moderate and severe forms of the disease, the inflammatory process leads to damage to the musculoskeletal system and cardiovascular system. Psoriasis has a recurrent course (recurrence of symptoms after complete or partial recovery) and a tendency to cause concomitant diseases that impair patients's quality of life.
Causes of psoriasis
The disease can be based on several causes. However, it is not yet known exactly which of them are primary and which are secondary. Immune system dysfunction is considered to be the main cause that explains the appearance of psoriasis. Cells that aim to destroy disease-causing agents begin to attack their own cells (mainly the skin). As a result, an inflammatory process develops, which causes accelerated division of epidermal cells (epidermal hyperplasia) and the formation of psoriatic papules and plaques.
An inadequate immune response is most often due to genetic characteristics.
Psoriasis is very often inherited.
Currently, more than 40 chromosome regions have been identified that are associated with the risk of developing psoriasis. The onset of the disease can be caused by a weakening of the immune system against the background of stress, infectious diseases, endocrine. Psoriasis often accompanies allergic and immunodeficiency conditions, which are based on a violation of the immune response. In addition, psoriasis can be caused by certain medications (antidepressants, beta-blockers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Classification of psoriasis
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, different types of psoriasis are distinguished. The most common is vulgar, eithercommon, psoriasiswhen well-defined pink papules appear on the skin, which clump together into plates covered with silvery-white scales. In case of scalp damage (psoriasis seborrheic) Yellow scaly rashes may descend to the forehead, forming a seborrheic "crown". In patients with metabolic disorders, plaques may exudate, a fluid secreted during inflammatory processes. exudative psoriasis). In childhood and adolescence, especially after streptococcal infections, the disease can become acute, with many bright red tear-shaped papules appearing on the skin with light skin and infiltration (psoriasis guttate). Sometimes there is pustular psoriasis, which is characterized by the appearance of pustules on the background of red skin, most often in the arch of the feet or palms.Psoriatic erythrodermacan occur against the background of worsening of common psoriasis under the influence of provocative factors. Dried white scales cover the skin, it becomes bright red, swollen and hot to the touch. He runs very hardgeneralized psoriasis Zumbusch. It is characterized by the fact that small purulent blisters appear on the red skin, which together form "purulent lakes".Psoriatic arthritisis associated with damage to the joints and develops simultaneously with redness or precedes them.
Symptoms of psoriasis
The skin form of psoriasis is accompanied by the appearance of papules with bright pink spots, sometimes in the form of spots. Together, they form plates covered with white silvery scales.
The rashes are located on the extensor surfaces of the arms and knee joints, on the scalp, in the lower back and sacrum.
The top layer of plaque is formed by dead epidermal scales that are easily removed. Initially, they occupy the center of the plate and then fill its entire area. When the scales are removed, a bright red surface appears. Sometimes the plaque is surrounded by a pink edge - an area of further growth, while the surrounding skin does not change. The rash is accompanied by intense itching. With psoriatic erythroderma, patients develop fever (chills with fever) and severe itching on the background of rashes all over the skin and swollen lymph nodes.
With a long course of the disease, hair and nails can fall out.
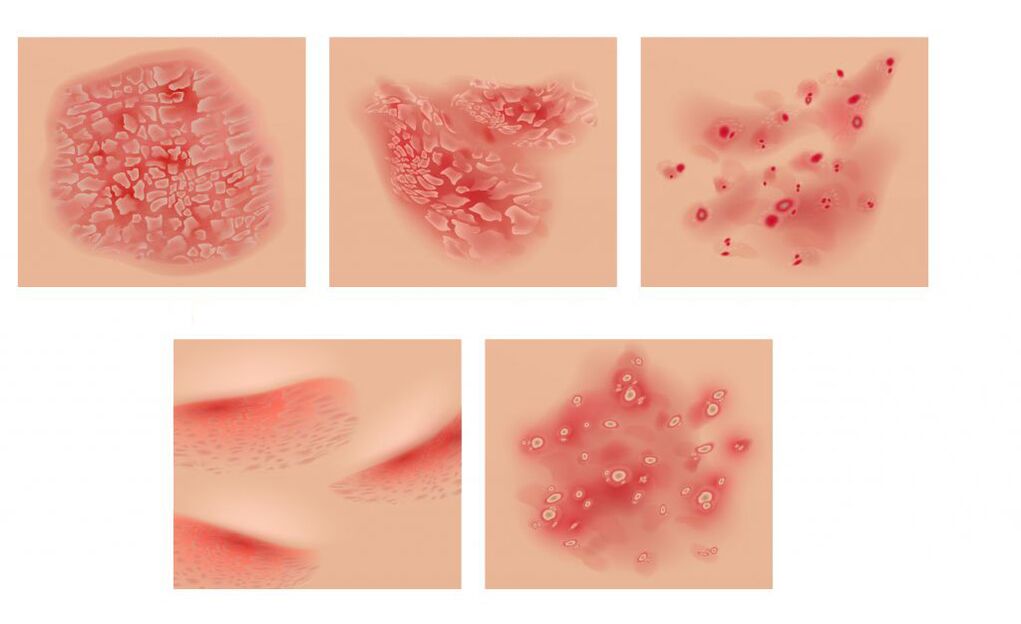
Generalized Zumbusch psoriasis is very difficult. Purulent flares cover the entire skin and are accompanied by severe fever and intoxication. Psoriatic joint damage is characterized by pain and redness of the skin over the articular surfaces. Every movement is difficult, inflammation of the ligaments and tendons develops. With psoriasis, nail plates are affected very often, while pronounced depressions appear on the surface of the nail (a "thimble" symptom).
Small, reddish and yellow-brown spots appear under the nail plate at the base (symptom of "oil stain"). Dystrophic changes in the nails and hair often develop.
In children, especially infants, the symptoms of psoriasis have their own specifics.
In the area of redness that appears on the skin folds, shedding and light skin of the upper layer of the epidermis may occur. This picture resembles diaper rash or candidiasis. Sometimes rashes appear on the skin of the face or in the genital area.
Diagnosis and psoriasis
It is possible to identify the disease based on the symptoms of the psoriatic triad (white stearic surface of the papule; reddish glossy film after removal of the scales and identification of lengthening of the blood after its removal).
An additional feature is the Koebner phenomenon. It lies in the fact that in the area of skin irritation, after 7-12 days appear erythematous-scaly rash (area of redness and skin in the area of scratches, abrasions). Sometimes, to confirm the diagnosis, a histological examination of a biopsy of the affected area of skin is performed. In addition, a clinical and laboratory examination is required: a clinical blood test, a biochemical blood test (total protein, protein fractions, C-reactive protein, ALT, AST, LDH, creatinine, electrolytes: potassium, sodium, chlorine, calcium).
Which doctors to contact
If rashes appear, which often occur against the background of infectious diseases, skin damage, stress, you should consult a therapist or dermatologist. In case of systemic damage to the patient's body, they may be referred to an ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist or other specialists.
Treatment
Psoriasis affects the skin and musculoskeletal system, as well as internal organs. When rashes appear only on the skin, topical glucocorticosteroid preparations, ointments containing synthetic analogues of vitamin D3, activated zinc, salicylic acid and other ingredients are recommended. Hormonal creams should be used with caution on skin prone to atrophy.
It is necessary to consider the possibility of hormonal disorders with prolonged use of steroid creams.
The effectiveness of hormonal creams increases in combination with salicylic acid, analogues of vitamin D. For the treatment of severe forms of psoriasis, second-generation aromatic retinoids, which are based on acitretin, are used. The drug slows down the proliferation of epidermal cells, normalizes the keratinization process and has an immunomodulatory effect. Phototherapy (medium UV and PUVA wave therapy) in combination with retinoids is also recommended. As a systemic therapy, the doctor may prescribe immunosuppressive agents. If necessary, prescribe detoxification and desensitizing therapy, plasmapheresis.
Complications of psoriasis
Psoriatic arthritis develops in 10% of patients, affecting the spine, arm and leg joints. Patients suffer from joint pain and stiffness in the morning. Characteristics of psoriatic arthritis include asymmetry of the sites of its manifestation, which can be combined with nail damage. Psoriasis is often associated with concomitant or comorbid diseases.
Due to inflammatory vascular lesions, the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke increases.
It is also possible to develop diabetes and Crohn's disease. In some cases, complications of psoriasis can lead to disability.
Prevention of psoriasis
Measures to prevent psoriasis are mainly aimed at strengthening the immune system. Skin care should include hydration and nourishment. With a predisposition to allergies, it is necessary to control food, avoiding fatty and spicy foods, excessive consumption of carbohydrates, potatoes. A mandatory component of psoriasis prevention should be vitamin therapy.
In addition, the functioning of the immune system depends largely on the state of the nervous system. People who are overly responsible, have a busy work schedule, and experience persistent negative psycho-emotional impact are more prone to autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis. Therefore, the prevention of psoriasis, along with physical therapeutic measures (giving up bad habits, physical activity), should also ensure the achievement of psycho-emotional comfort.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other worsening of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For proper diagnosis and treatment, you should contact your doctor.