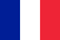
What is psoriasis and what does it look like?Psoriasis is the non -infectious condition of the skin, the result of which are red slabs, as well as dry scales - the result of extremely rapid growth of skin cells.The disease most often affects the skin on the elbows, knees and scalp.
In some people, it manifests itself in a mild form, symptoms are practically absent.Others mark severe symptoms, frequent relapses.From what is psoriasis, where it seems, the causes of appearance, how they become infected - we will try to answer these and other questions on the pages of our portal.
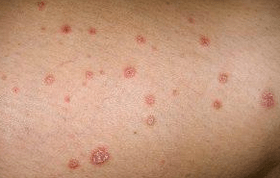
Psoriasis is an incurable, long -term (chronic) condition of the skin.The stages of irritation are rapidly replaced by the stages of improvement.Many patients mark the worsening of symptoms from November to February (winter months) as well as in hot summer time.Psoriasis affects all ethnic races and representatives of both sexes.Although psoriasis can occur in people of any age - from infants to the elderly - most often the disease is diagnosed in adolescence under 20 years.
At what age does psoriasis appear?The disease is rare in infants (less than 4% of the patients), in children psoriasis can occur if parents are carriers of the disease.Psoriasis in such young children is often preceded by acute pharyngitis, tonsils, bronchitis or respiratory infection, for example, a cold, flu or pneumonia.People with psoriasis have more chances of getting diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease.
Why does psoriasis occur?The causes of psoriasis are unknown to the end, but the disease is usually associated with the immune system problem.From what and how psoriasis does it appear?The main element is a special type of lymphocytes, called T-lymphocytes or T cells. As a rule, these white blood cells move throughout the body to detect and eliminate foreign substances, such as viruses or parasites (Streptococcus).However, in patients with psoriasis, T-lymphocytes mistakenly attack healthy skin cells (to combat a false infection).
Hyperactive lymphocytes provoke immune reactions, including enlargement and growth of the vessels around the papule and pustules of passriasis.These changes lead to an increase in the production of healthy skin cells and other white blood cells.This causes a continuous cycle, against which new skin cells move to the upper layers of the epidermis very quickly - within a few days.
Researchers also found genes related to the development of psoriasis, proving that the disease is inherited, but external environmental factors (physical, chemical, thermal effect on the skin) and internal (stress, unbalanced nutrition, daytime violation, infection, excessive/regular use of alcohol and smoking) also play a certain role.
Signs and symptoms
Psoriasis manifests itself in the form of red or pink scales cones that join in large skin papules (plates).Sometimes, when combing these small dry white scales, slight bleeding occurs.
There are several types of psoriasis - not pustular (affects large areas of the skin) and pustular (rarer, usually manifested in the hands or feet).Redness can have different sketches and spots and rocky shapes to a visible monetary.
The first signs of psoriasis are increased fatigue, weakness throughout the body, sometimes a slight dizziness, general mistreatment.As the rashes develop and increase, symptoms such as itching, burning, pain, sometimes fever, chills.
PHASE
In the absence of treatment, psoriasis develops quite quickly.In the initial stage, small pink or reddish scales appear on the skin (which are usually symmetrically located, for example, in both hands the dots will be placed in the same way).Further, at the top of the reddish points, a scaly surface layer begins to develop.
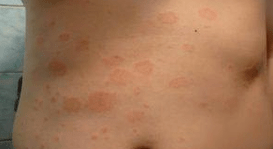
This is keratinized skin, which is easily removed independently.After the formation of scales, the red stains are collected on large red plates, this stage is associated with severe itching and burns, as well as peel of the skin.
irritation
The deterioration phase is characterized by the appearance of large (often swollen) spots on the skin (plaque, dad), severe itching, burns, often pain.The area of spreading the disease also increases significantly (plaques become more than 10 cm in diameter).A special feeling of tightening the skin appears.When moving the disease to the irritation stage, you should contact a specialist immediately.During this phase, the cracks appear on the skin (due to tightening, dryness and keratinization).
The danger to life
During the worsening phase, cracks in dry keratinized areas, the skin begins to bleed and becomes more susceptible to infections, which causes new plaques (Köbner syndrome).
The most severe consequence of irritation can be psoriatic arthritis (the disease will spread to the bones and joints and cause their inflammation and deformity) or psoriatic erythroderma (a very serious skin disease, which can lead to death).
Psoriasis continues to be one of the most complex skin diseases.A wide range of procedures available for the treatment of psoriasis illustrates this.It is very important to take measures to curb the disease and prevent it from going to the irritation phase, so it is necessary to seek help from a specialist, as well as change your lifestyle, turn to the medicines and methods of traditional medicine.